



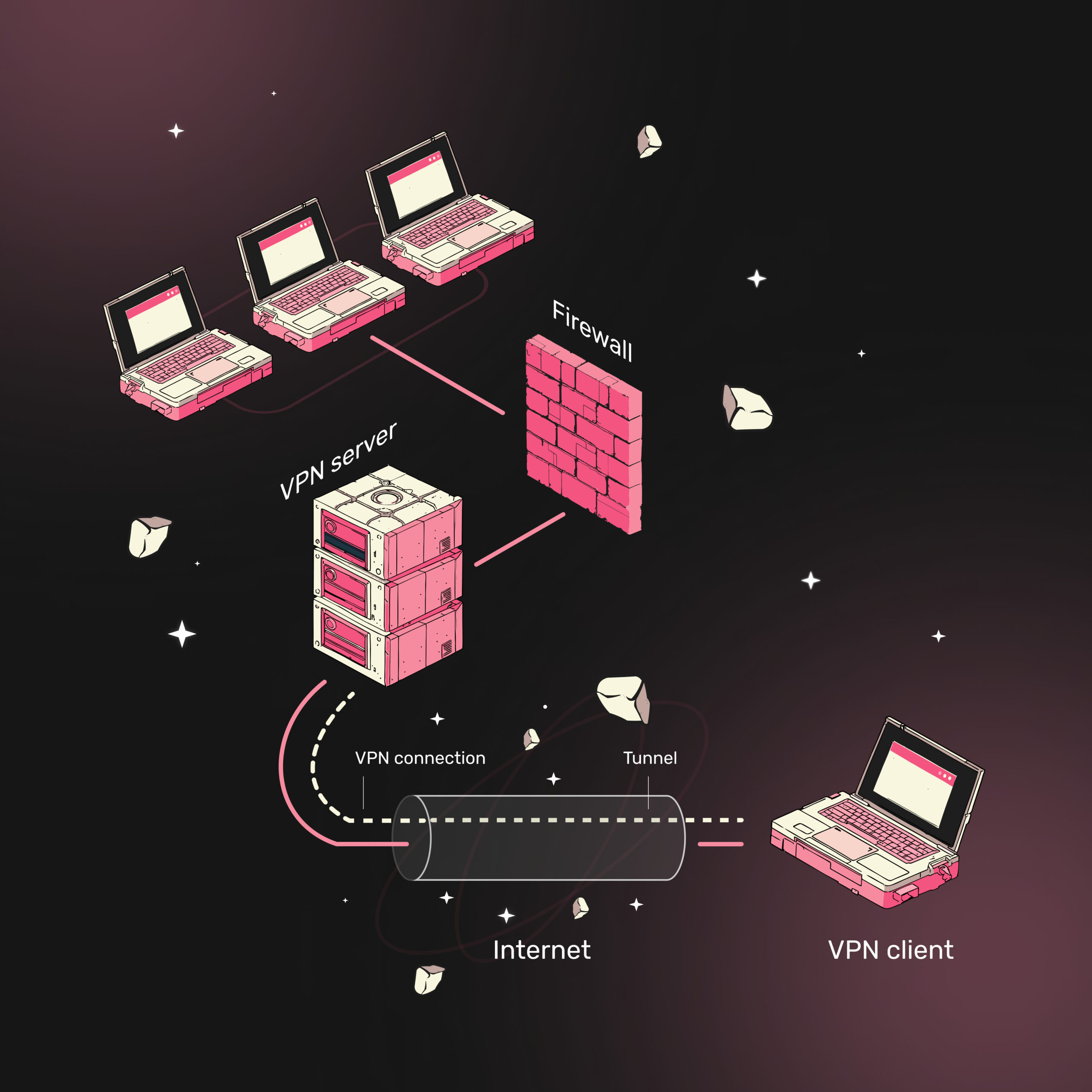
A firewall is a fundamental component of network security designed to monitor, filter, and regulate incoming and outgoing network traffic. It operates based on predefined security rules to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate cyber threats. Acting as a protective barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks such as the Internet, firewalls play a vital role in ensuring secure communication and data protection.
Firewalls can be classified based on their deployment and functionality:
According to NIST Special Publication 800-10, firewalls can be broadly categorized into three primary types based on their filtering techniques:
Packet filtering firewalls are the most basic type of firewall and operate at Layer 3 (Network Layer) and Layer 4 (Transport Layer) of the OSI model. They inspect packets based on parameters such as:
These firewalls use Access Control Lists (ACLs) to allow or block traffic. However, since they do not track the state of connections, they are susceptible to attacks such as IP spoofing.
Stateful inspection firewalls enhance security by tracking the state of active connections. They maintain a state table containing details such as IP addresses, port numbers, and session states. Only packets that belong to legitimate and established connections are permitted, making stateful firewalls more secure than basic packet filtering firewalls.
A proxy firewall operates at the Application Layer (Layer 7) of the OSI model and acts as an intermediary between the client and the server. By processing requests on behalf of users, it prevents direct communication between internal and external networks. Proxy firewalls perform deep packet inspection, allowing them to effectively detect and block malicious content.
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) establishes a secure, encrypted tunnel over the public Internet, allowing users to access private networks remotely. VPNs ensure confidentiality, integrity, and authentication, making them essential for privacy and secure communication.
VPNs secure data using encryption and tunneling protocols. Common VPN protocols include:
| Feature | Firewall | VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Filters and monitors traffic | Encrypts communication |
| Security Layer | Network/Application Layer | Network Layer |
| Protection | Blocks unauthorized access and malware | Prevents data interception |
| Use Case | Corporate networks, data centers | Remote access, secure browsing |
| Performance Impact | May slow traffic due to filtering | May reduce speed due to encryption |
| Configuration | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Cost | Hardware/software-based | Subscription or free options |
Using firewalls and VPNs together provides layered security:
Firewalls and VPNs serve distinct yet complementary roles in cybersecurity. While firewalls protect networks by regulating traffic and preventing unauthorized access, VPNs secure communication through encryption and privacy protection. Implementing both technologies together creates a robust and comprehensive security framework.
By understanding and correctly deploying firewalls and VPNs, organizations and individuals can significantly enhance cybersecurity, safeguard sensitive data, and ensure secure remote access. Proactive security measures today are essential for preventing future data breaches and cyberattacks.